Gas Turbine Generators
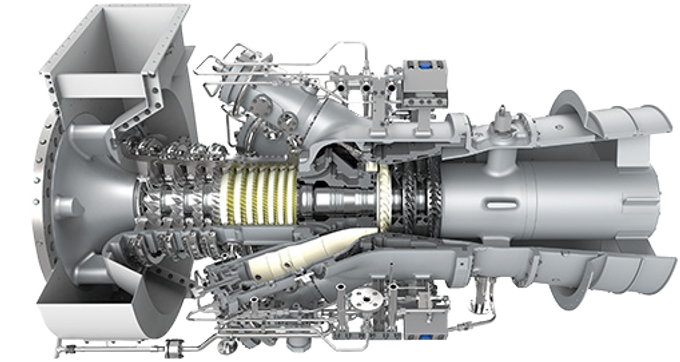
Gas turbine generators are widely used in the upstream oil and gas industry to provide reliable, high-capacity power for a variety of field operations, particularly in remote or off-grid environments. These systems utilize a combustion-driven turbine to convert natural gas or liquid fuels into mechanical energy, which then drives an electrical generator. The technology is valued for its ability to deliver large amounts of power with rapid startup times, high operational efficiency, and a relatively compact footprint.
In upstream applications, gas turbine generators are commonly deployed to support drilling rigs, production facilities, and processing plants, supplying essential electricity for pumps, compressors, control systems, and accommodation units. Their robust design enables them to operate efficiently under harsh ambient conditions and fluctuating fuel quality, making them ideal for oil fields where other power sources may be unreliable or unavailable. Additionally, gas turbines can often be fueled by associated gas produced onsite, helping operators reduce flaring and improve overall energy efficiency.
Key advantages of gas turbine generators in oil and gas operations include their high power output, ability to run on multiple fuel types, low maintenance requirements, and suitability for continuous or peaking power demands. Their flexibility, reliability, and environmental benefits make them a preferred choice for powering critical upstream infrastructure.